Non-overlapping clock generator
This article contains Verilog-A models for a Non-overlapping clock generator.
Table of Contents
- Non-overlap clock generator (same as clk)
- Non-overlap clock generator with 2 phases
- Non-overlap clock generator with 4 phases
Usage:
- Create a new cell in Library Manager named nonoverlap_clk and select cell type Verilog A;
- Copy and paste the code provided;
- Specify vdd and vss variables to reflect high/low levels of the clk;
- Specify t_edge and t_delay variables to be the rising/falling time and delay of the output waveform;
- Specify t_dead to define the dead time between phases;
- Perform Check and Save;
- A cell symbol will be created;
- Instantiate nonoverlap_clk cell into your design;
- Perform Check and Save and run the simulation.
Non-overlapping clock generator (same as clk)
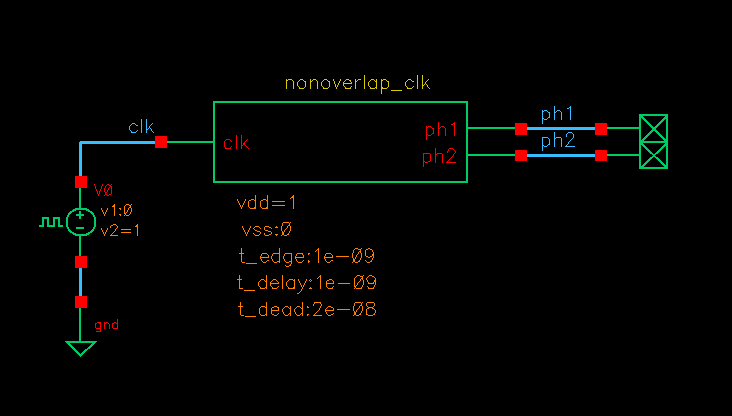
Nonoverlap_clk testbench
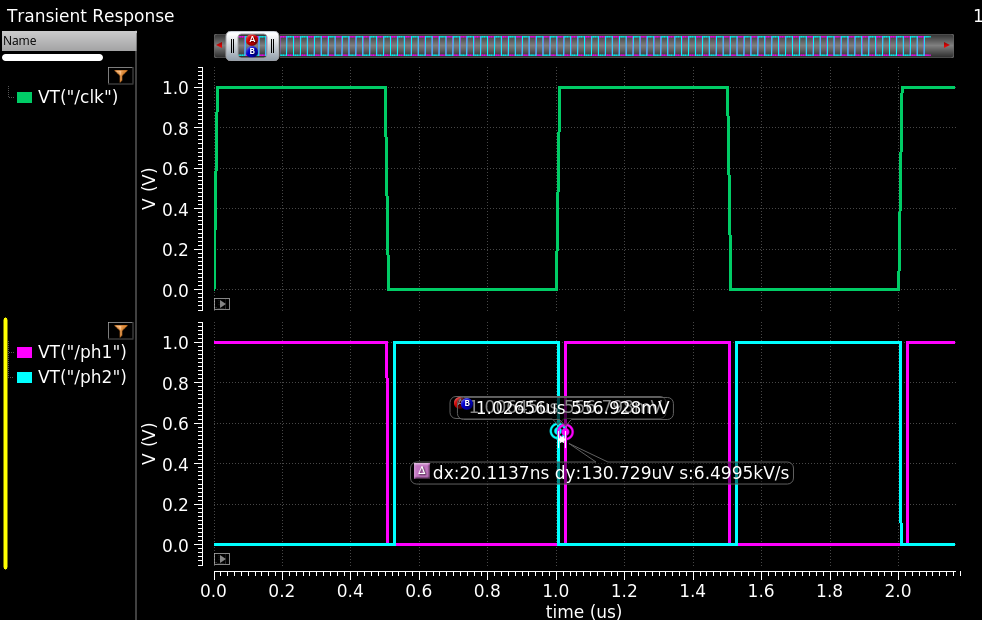
Nonoverlap_clk simulation result
Cell name: nonoverlap_clk
Model type: Verilog-A
1// Non-overlap clock generator (same freq as clk)
2// Author: A. Sidun
3// Source: AnalogHub.ie
4
5\`include "constants.vams"
6\`include "disciplines.vams"
7
8module nonoverlap_clk (clk, ph1, ph2);
9 input clk;
10 output ph1, ph2;
11 electrical clk, ph1, ph2;
12
13 parameter real vdd = 5.0;\t\t// define clock high
14 parameter real vss = 0.0;\t\t// define clock low
15 parameter real t_edge = 1e-9;\t// rising/falling edge of ph1/ph2
16 parameter real t_delay = 1e-9;\t// delay from the input clock edge for ph1/ph2
17 parameter real t_dead = 20e-9; \t// dead-time between ph1/ph2
18
19 real delay_ph1;
20 real delay_ph2;
21 real d_ph1;
22 real d_ph2;
23
24analog begin
25@(initial_step) begin
26 d_ph1 = 1;
27 d_ph2 = 0;
28 end
29
30@(cross(V(clk)-vdd/2, +1)) begin\t//rising edge of clk
31 d_ph1 = 1;
32 d_ph2 = 0;
33\t\tdelay_ph1 = t_delay + t_dead;
34\t\tdelay_ph2 = t_delay;
35end
36
37@(cross(V(clk)-vdd/2, -1)) begin\t//falling edge of clk
38 d_ph1 = 0;
39 d_ph2 = 1;
40\t\tdelay_ph1 = t_delay;
41\t\tdelay_ph2 = t_delay + t_dead;
42end
43
44V(ph1) <+ vdd*transition(d_ph1,delay_ph1,t_edge) + vss*transition(d_ph2,delay_ph1,t_edge);
45V(ph2) <+ vdd*transition(d_ph2,delay_ph2,t_edge) + vss*transition(d_ph1,delay_ph2,t_edge);
46
47end //analog begin
48endmoduleNon-overlapping clock generator with 2 phases
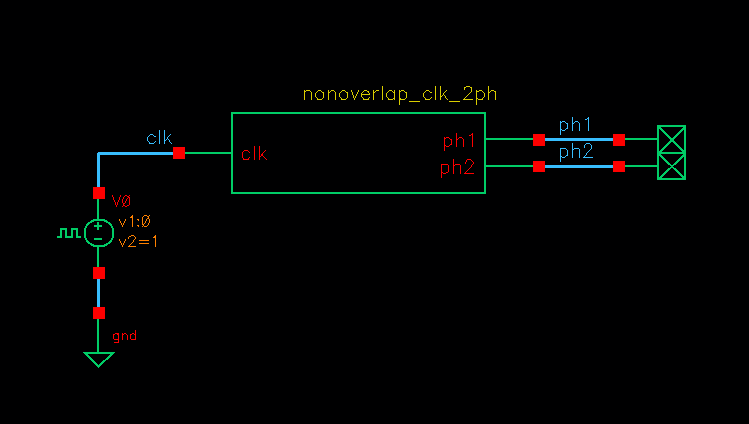
2-phases nonoverlap_clk testbench
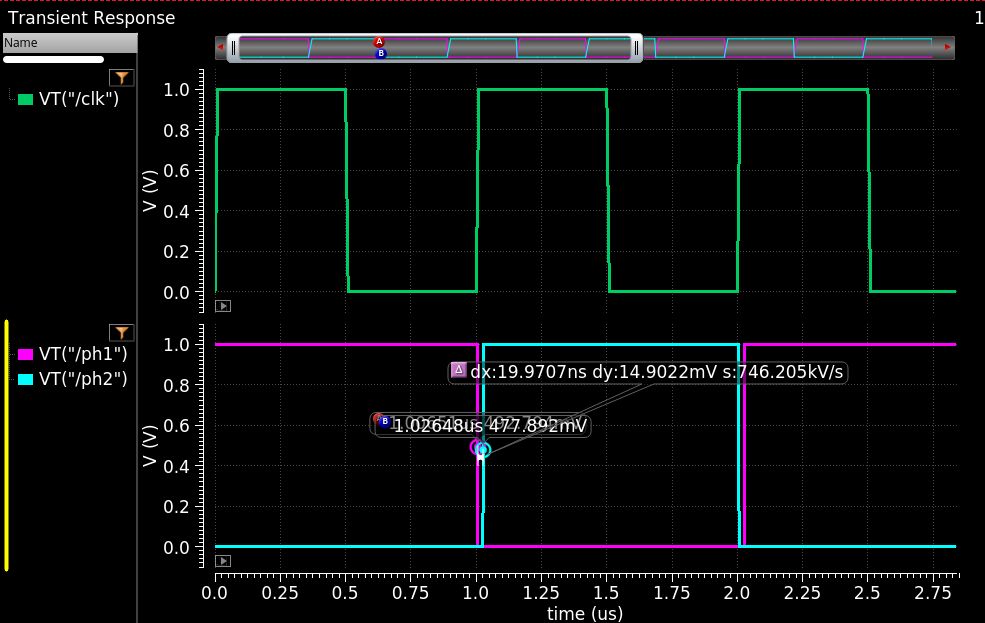
2-phases nonoverlap_clk simulation result
Cell name: nonoverlap_clk_2ph
Model type: Verilog-A
1// Non-overlap clock generator (frequency-divided)
2// Author: A. Sidun
3// Source: AnalogHub.ie
4
5\`include "constants.vams"
6\`include "disciplines.vams"
7
8module nonoverlap_clk_2ph (clk, ph1, ph2);
9 input clk;
10 output ph1, ph2;
11 electrical clk, ph1, ph2;
12
13 \tparameter real vdd = 5.0; // define clock high
14 parameter real vss = 0.0;\t// define clock low
15\tparameter real t_edge = 1e-9; // rising/falling edge of ph1/ph2
16\tparameter real t_delay = 1e-9; // delay from the input clock edge for ph1/ph2
17 parameter real t_dead = 20e-9; // dead-time between ph1/ph2
18
19 real delay_ph1;
20 real delay_ph2;
21 real d_ph1;
22 real d_ph2;
23 integer counter_ph1=0;
24
25analog begin
26@(initial_step) begin
27 d_ph1 = 1;
28 d_ph2 = 0;
29 end
30
31
32@(cross(V(clk)-vdd/2, +1)) begin\t//rising edge of clk
33 counter_ph1 = counter_ph1 + 1; // count rising edges
34\t\t$display("Rising edge number: %d", counter_ph1);
35 case(counter_ph1)
36 1: begin
37 d_ph1 = 1;
38 d_ph2 = 0;
39 delay_ph1 = t_delay + t_dead;
40\t\t delay_ph2 = t_delay;
41 end
42 2: begin
43 d_ph1 = 0;
44 d_ph2 = 1;
45 delay_ph1 = t_delay;
46\t\t delay_ph2 = t_delay + t_dead;
47 counter_ph1 = 0; // reset counter
48 end
49endcase
50end
51
52
53/*@(cross(V(clk)-vdd/2, -1)) begin\t//falling edge of clk
54 d_ph1 = 0;
55 d_ph2 = 1;
56\t\tdelay_ph1 = t_delay;
57\t\tdelay_ph2 = t_delay + t_dead;
58end */
59
60V(ph1) <+ vdd*transition(d_ph1,delay_ph1,t_edge) + vss*transition(d_ph2,delay_ph1,t_edge);
61V(ph2) <+ vdd*transition(d_ph2,delay_ph2,t_edge) + vss*transition(d_ph1,delay_ph2,t_edge);
62
63end //analog begin
64endmoduleNon-overlapping clock generator with 4 phases
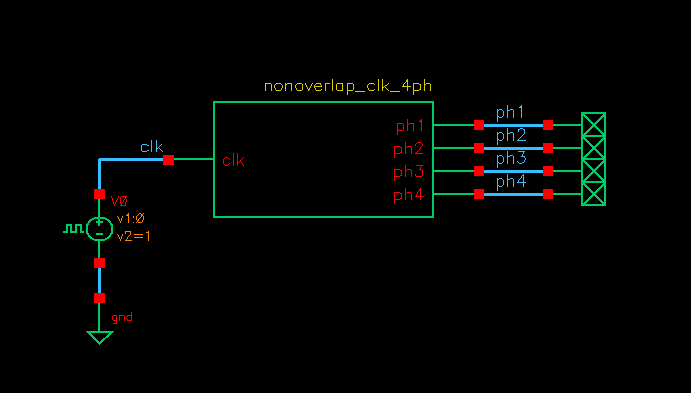
4-phases nonoverlap_clk testbench
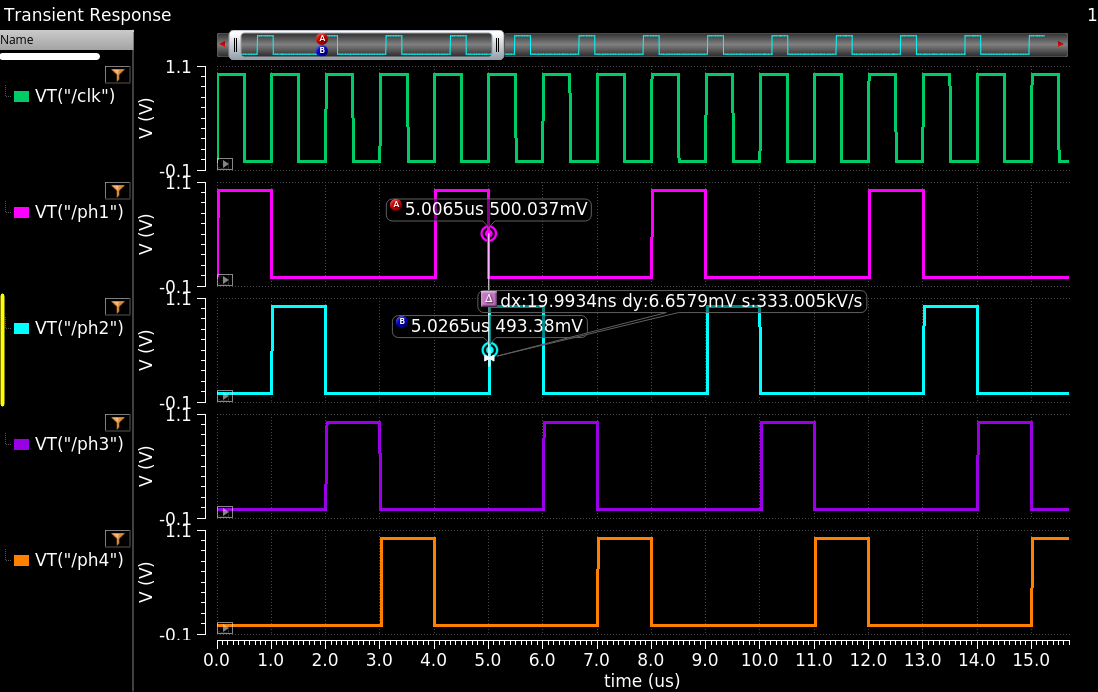
4-phases nonoverlap_clk simulation result
Cell name: nonoverlap_clk_4ph
Model type: Verilog-A
1// 4-phases non-overlap clock generator
2// Author: A. Sidun
3// Source: AnalogHub.ie
4
5// ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____
6// CLK ____| |____| |____| |____| |____| |____| |____
7// _________ _________
8// PH1 ____| |_____________________________| |_______________
9// _________ _________
10// PH2 ______________| |_____________________________| |_______________
11// _________ _________
12// PH3 ________________________| |_____________________________| |_______________
13// _________ _________
14// PH4 __________________________________| |_____________________________| |_______________
15
16// Non-overlap clock generator (frequency-divided)
17
18\`include "constants.vams"
19\`include "disciplines.vams"
20
21module nonoverlap_clk_4ph (clk, ph1, ph2, ph3, ph4);
22 input clk;
23 output ph1, ph2, ph3, ph4;
24 electrical clk, ph1, ph2, ph3, ph4;
25
26 \tparameter real vdd = 1.0; // define clock high
27 parameter real vss = 0.0;\t// define clock low
28\tparameter real t_edge = 1e-9; // rising/falling edge of ph1/ph2
29\tparameter real t_delay = 1e-9; // delay from the input clock edge for ph1/ph2/ph3/ph4
30 parameter real t_dead = 20e-9; // dead-time between ph1/ph2/ph3/ph4
31
32 real delay_ph1;
33 real delay_ph2;
34 real delay_ph3;
35 real delay_ph4;
36 real bit_ph1;
37 real bit_ph2;
38 real bit_ph3;
39 real bit_ph4;
40 integer clk_edge_count=0; // clock rising edge counter
41
42analog begin
43@(initial_step) begin
44 bit_ph1 = 0;
45 bit_ph2 = 0;
46 bit_ph3 = 0;
47 bit_ph4 = 0;
48 end
49
50
51@(cross(V(clk)-vdd/2, +1)) begin\t//rising edge of clk
52 clk_edge_count = clk_edge_count + 1; // count rising edges
53\t\t//$display("Rising edge number: %d", clk_edge_count);
54 case(clk_edge_count)
55 1: begin
56 bit_ph1 = 1;
57 bit_ph2 = 0;
58 bit_ph3 = 0;
59 bit_ph4 = 0;
60\t\t\tdelay_ph4 = t_delay;
61 delay_ph1 = t_delay + t_dead;
62 end
63 2: begin
64 bit_ph1 = 0;
65 bit_ph2 = 1;
66 bit_ph3 = 0;
67 bit_ph4 = 0;
68\t\t\tdelay_ph1 = t_delay;
69\t\t delay_ph2 = t_delay + t_dead;
70
71 end
72 3: begin
73 bit_ph1 = 0;
74 bit_ph2 = 0;
75 bit_ph3 = 1;
76 bit_ph4 = 0;
77\t\t\tdelay_ph2 = t_delay;
78\t\t\tdelay_ph3 = t_delay + t_dead;
79
80 end
81 4: begin
82 bit_ph1 = 0;
83 bit_ph2 = 0;
84 bit_ph3 = 0;
85 bit_ph4 = 1;
86\t\t\tdelay_ph3 = t_delay;
87\t\t\tdelay_ph4 = t_delay + t_dead;
88 clk_edge_count = 0; // reset counter
89 end
90endcase
91end
92
93V(ph1) <+ vdd*transition(bit_ph1,delay_ph1,t_edge) + vss*transition(bit_ph2,delay_ph1,t_edge);
94V(ph2) <+ vdd*transition(bit_ph2,delay_ph2,t_edge) + vss*transition(bit_ph1,delay_ph2,t_edge);
95V(ph3) <+ vdd*transition(bit_ph3,delay_ph3,t_edge) + vss*transition(bit_ph3,delay_ph3,t_edge);
96V(ph4) <+ vdd*transition(bit_ph4,delay_ph4,t_edge) + vss*transition(bit_ph4,delay_ph4,t_edge);
97
98end //analog begin
99endmodule